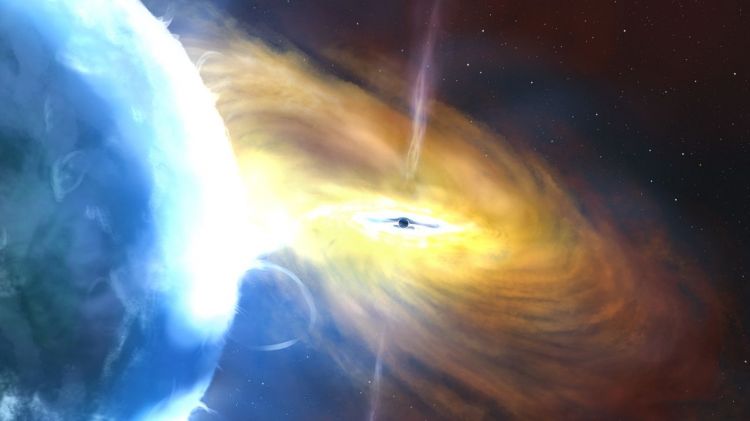
Astronomers have discovered what they believe to be the largest explosion ever detected.
EDnews informs via CNN that the explosion is more than 10 times brighter than any recorded exploding star - known as a supernova.
So far it has lasted more than three years, much longer than most supernovae which are usually only visibly bright for a few months.
One theory is that the blast was caused when a vast cloud of gas was swallowed up by a black hole.
A flash in the sky was first automatically detected and recorded in 2020 by the Zwicky Transient Facility in California. But it wasn't until a year later that it was picked up by astronomers combing through the data.
They called the event AT2021lwx. At the time they thought it was unremarkable because there was no indication of how far away it was and therefore it wasn't possible to calculate its brightness.
Last year a team led by Dr Philip Wiseman from the University of Southampton analysed the light from the event which enabled them to calculate its distance - 8bn light years away. Dr Wiseman described the moment the worked out the brightness of the phenomenon.
"We thought 'oh my God, this is outrageous!'".