Jellyfish have a bad rep. Most people are disgusted by or even afraid of them. But the squishy sea-dwellers are beautiful creatures - who don't even need a brain to gracefully float through the seas.

Jellyfish have been floating around the Earth's oceans for 500 million years now - without a brain to guide them. Jellyfish use their sophisticated nervous system which immediately translates outside impulses into action. That's why this rhizostome jellyfish and its relatives don't need a brain to process information.

Medusa of the seas
Jellyfish live in the sea. But the name is misleading - they're not actually fish. They're members of the cnidaria phylum and are related to corals and anemones. They're also classified as medusozoa - with the tentacles floating around their bodies, they look a little like the Greek monster Medusa, who had living snakes instead of hair on her head.

Umbrella with tentacles
A jellyfish body contains up to 99 percent water. Human bodies only contain around 63 percent water. A big part of the jellyfish is its umbrella-shaped bell. Attached to that is the manubrium, through which the animal takes up nutrients, and hundreds of tentacles. With some jellyfish, the tentacles can be a couple of meters long. The animals use them to feel their way around and to hunt prey.

Giant jellyfish
Most jellyfish are white or transparent. There are also some exceptional jellyfish species out there, though. The Asian Nomura's jellyfish isn't especially colorful, but it's huge: it has a diameter of up to two meters (6.5 feet) and can weigh more than 200 kilograms (440 pounds).

Follow the current
Scientists consider jellyfish plankton because they're swept along by the current of the sea. The jellyfish isn't great at getting anywhere by itself. It propels itself forward by constricting and relaxing its bell, achieving speeds of up to 10 kilometers per hour (6 mph). Even bugs walk faster.
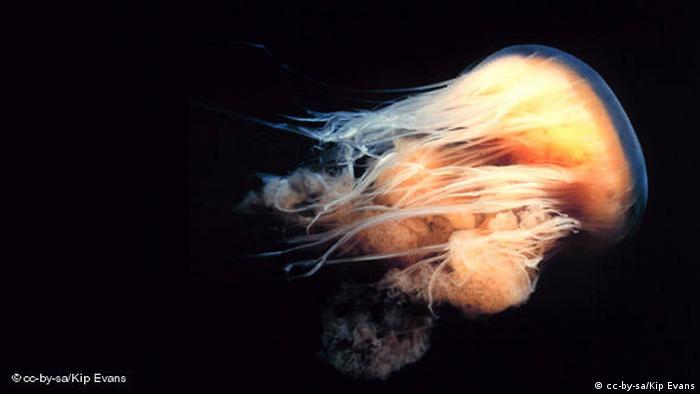
Pretty and poisonous
Jellyfish might look graceful floating through water like squishy goasts, but some of them have extremely dangerous tentacles - like this lion's mane jellyfish. Their tentacles are covered in nematocysts. The animal injects the stinging cells into its prey and kills them with the toxic injection. Plankton, algae, small crabs and fish larvae are all on the menu.

Stranded
If you find a sad blob like this on the beach, it's most likely a jellyfish out of its natural habitat. If you want to do a good deed, grab some gloves for protection and deliver the animal back into the sea. Don't touch it with your bare hands, don't step on it and don't toss it onto your unsuspecting girlfriend while she's sunbathing.

Jellyfish carpaccio
Beach towns often have to deal with jellyfish invasions. Bioligists believe this is due to overfishing and the decline of sea turtles and jellyfish-eating fish. But the squishy sea-dweller is also gaining popularity as a delicacy on restaurant tables. It has no natural aroma, which makes it the perfect flavor carrier.